During a five-month period from 2022 to 2023, Massachusetts Air National Guard member Jack Teixeira sent 40,000 messages on the online chat platform Discord, some of which contained classified national security secrets.
An FBI investigation revealed that Teixeira, a 22-year-old who ran a server on Discord called “Thug Shaker Central,” spent much of his life online, talking primarily with other young men via message, video calls and voice chats. He chatted about guns and military gear, threatened his school, made racist and antisemitic jokes, traded conspiracy theories, discussed antigovernment sentiments, and in a bid to show off, shared some of the military’s most closely guarded secrets about the Russia-Ukraine war and the Middle East.
By the time the young airman was arrested in 2023, media scholar PS Berge had been studying Discord and its users for three years and had created an online consortium of other academic researchers who were doing the same. That an intelligence leak occurred on the site, creating a national security incident, didn’t come as a shock to her.
“My response was, ‘Of course. Of course this would happen on Discord,’” Berge said. “Because on a platform like this, you share everything with your people. Everything about your life. So, why not share national security secrets?”
Teixeira pleaded guilty in March to six counts of willful retention and transmission of national defense information. His sentencing is scheduled for September, and prosecutors are asking that he serve between 11 and 17 years in prison.

The same month Teixeira agreed to a plea deal, the FBI revealed it had investigated another service member in 2022 for leaking information on Discord.
Former Air Force Staff Sgt. Jason Gray, who served as a cyber analyst at Joint Base Elmendorf-Richardson, Alaska, admitted to running a Facebook group for followers of Boogaloo, a loosely organized, antigovernment movement that advocates for a second Civil War. Gray was disgruntled with his military career, and he discussed his dissatisfaction with the U.S. government in several Discord channels created for the Boogaloo movement, according to a 2022 FBI affidavit that was unsealed in March.
Gray, who used the account name LazyAirmen#7460, was accused of posting a classified image in a private Discord channel that he “likely obtained” from his access to National Security Agency intelligence, the affidavit states.
Investigators said the image could’ve been shared “in furtherance of the Boogaloo ideology,” but didn’t elaborate on the image’s details. It’s uncertain whether the FBI is still investigating the potential leak. But while searching Gray’s electronic devices for evidence of an intelligence breach, authorities discovered hundreds of images of child pornography. Gray is currently serving five years in federal prison on multiple child pornography charges.
Oversharing is a hallmark of Discord, an online world where members of certain channels talk all day, every day, and even fall asleep together on voice calls, said Megan Squire, a computer scientist and deputy director for data analytics at the Southern Poverty Law Center.
People who study the platform agree that it’s not inherently bad — it’s used by millions of gamers, students, teachers, professionals, hobbyists and members of the military community to communicate and socialize. However, extremists have hijacked a part of the platform to radicalize and recruit others to their causes, said Jakob Guhl, senior manager for policy and research at the Institute for Strategic Dialogue.
Following the leak of national security secrets and other high-profile, nefarious uses of the platform in recent years, researchers are grappling with what to think of the platform’s small but headline-grabbing dark side, and many disagree on whether Discord as a company is doing enough to root out bad actors.
“It’s always a bit difficult to strike the right tone between not scaring people off the platform, because the majority of users are completely fine, but also highlighting that there is an actual issue of radicalization,” Guhl said. “It’s not the biggest or most offending platform, but it definitely plays a crucial role among this network.”

‘Not inherently evil’
The National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism, known as START, studied decades of violent extremist attacks and found a military background to be the most commonly shared characteristic among those who committed or plotted mass casualty attacks from 1990 through 2022, more so than criminal histories or mental health problems.
Researchers from START said the study revealed why extremist groups tend to focus recruitment efforts toward people with military service records: Even a small number of them can have an outsized impact inside extremist movements.
While such recruitment occurs on Discord, Guhl, Berge and Squire agreed that the mere presence of service members and veterans on the platform isn’t a cause for concern.
“It’s a popular platform and not inherently evil,” Squire said. “I’d be much more concerned about military folks on 4chan, Telegram, places like that. Nothing good is happening on those platforms, but Discord could be useful.”
In fact, Berge said, it can be a valuable forum for marginalized people to foster a sense of community. On its “about” page, Discord describes its mission as one that helps users find a sense of belonging.
“Discord is about giving people the power to create space to find belonging in their lives,” the company’s mission statement reads. “We want to make it easier for you to talk regularly with the people you care about. We want you to build genuine relationships with your friends and communities close to home or around the world.”
That’s what the veterans group Frost Call is doing on the platform. The nonprofit encourages veterans and service members to stay connected through gaming, one of its founders told Military Times last year. As of June, it boasted 390 members.

“When we founded Frost Call, we built an organization around this idea of bringing veterans together, helping to improve camaraderie that’s missing from military service,” Marine Corps veteran Wesley Sanders said last year. “It serves an enormous mental health need, but also ... an existential need for a lot of veterans.”
Moreover, when new users join Discord, extremist elements of the platform are not easily visible.
Discord is made up of millions of servers centered on various topics. Users can join up to 100 servers, and each server has numerous text, voice and video channels. When a new user creates an account and searches servers to join, the platform will suggest “its most popular, most successful, public-facing communities,” rather than any disquieting, invite-only communities, Berge said.
“If you are a standard user, and if you’re signing in to Discord for your general interests — maybe you’re looking for fellow students or fellow veterans — 90% of the time, you’re not going to accidentally stumble upon an extremist group,” she said. “They actually go through a lot of effort to make these spaces insulated, to make them difficult to find.”
When using Disboard, a third-party search platform for Discord servers, prompts such as “Nazi” or “white supremacist” won’t elicit results like they used to, Berge said. In a 2021 study, she found thousands of Discord servers that marketed themselves on Disboard as hateful and Nazi-affiliated spaces.
“You used to be able to search for those terms and find communities. It was horrifying,” Berge said. “Those servers still exist, but they’ve changed the ways they’re identified, and in some cases, we know that high-profile, toxic communities have been shut down.”
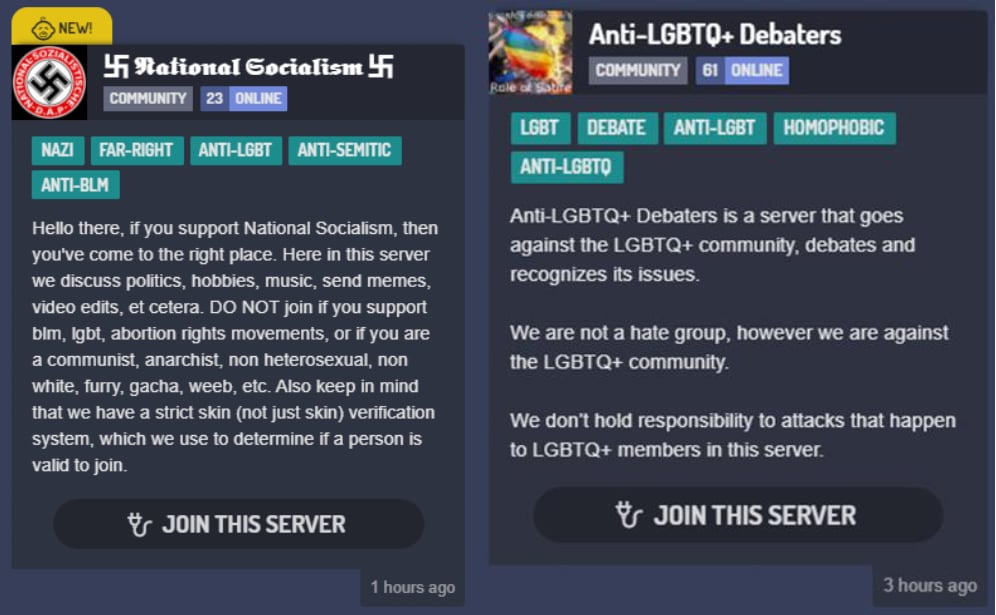
Extremists find a foothold
Founders Jason Citron and Stan Vishnevskiy created Discord in 2015 as a way to allow friends around the world to communicate while playing video games online. Its popularity exploded during the Covid-19 pandemic, when lockdowns went into effect and many people became more isolated than ever before.
Just two years after it launched, Discord gained notoriety as the platform of choice for facilitators of the 2017 “Unite the Right” rally in Charlottesville, Virginia. Organizers, including some veterans, used Discord to share propaganda and coordinate the protest, which turned deadly. James Fields was convicted of killing Heather Heyer when he drove his car into a group of counterprotesters. Fields had joined the Army in 2015 but was separated quickly because of a cited lack of motivation and failure to train.
In 2022, Discord made headlines again after a mass shooting at an Independence Day parade in Highland Park, Illinois, where seven people were killed and dozens more injured. The suspected shooter ran his own Discord server called “SS,” where he complained about “commies,” short for “communists,” according to posts archived by the nonprofit website Unicorn Riot.
That same year, an 18-year-old white gunman killed 10 Black people at a supermarket in Buffalo, New York. The gunman, Payton Gendron, spent months writing plans for the attack in a diary he kept on a private Discord server, visible only to him. About 30 minutes before the attack, Gendron sent out invitations for others to view the diary, and 15 people accessed it, according to Discord.
The platform again faced scrutiny following Teixeira’s leak of national security secrets.
“It’s periodic. Every couple of years, it seems like there’s something,” Squire said. “There are other platforms that are worse, but Discord keeps coming up over and over again.”
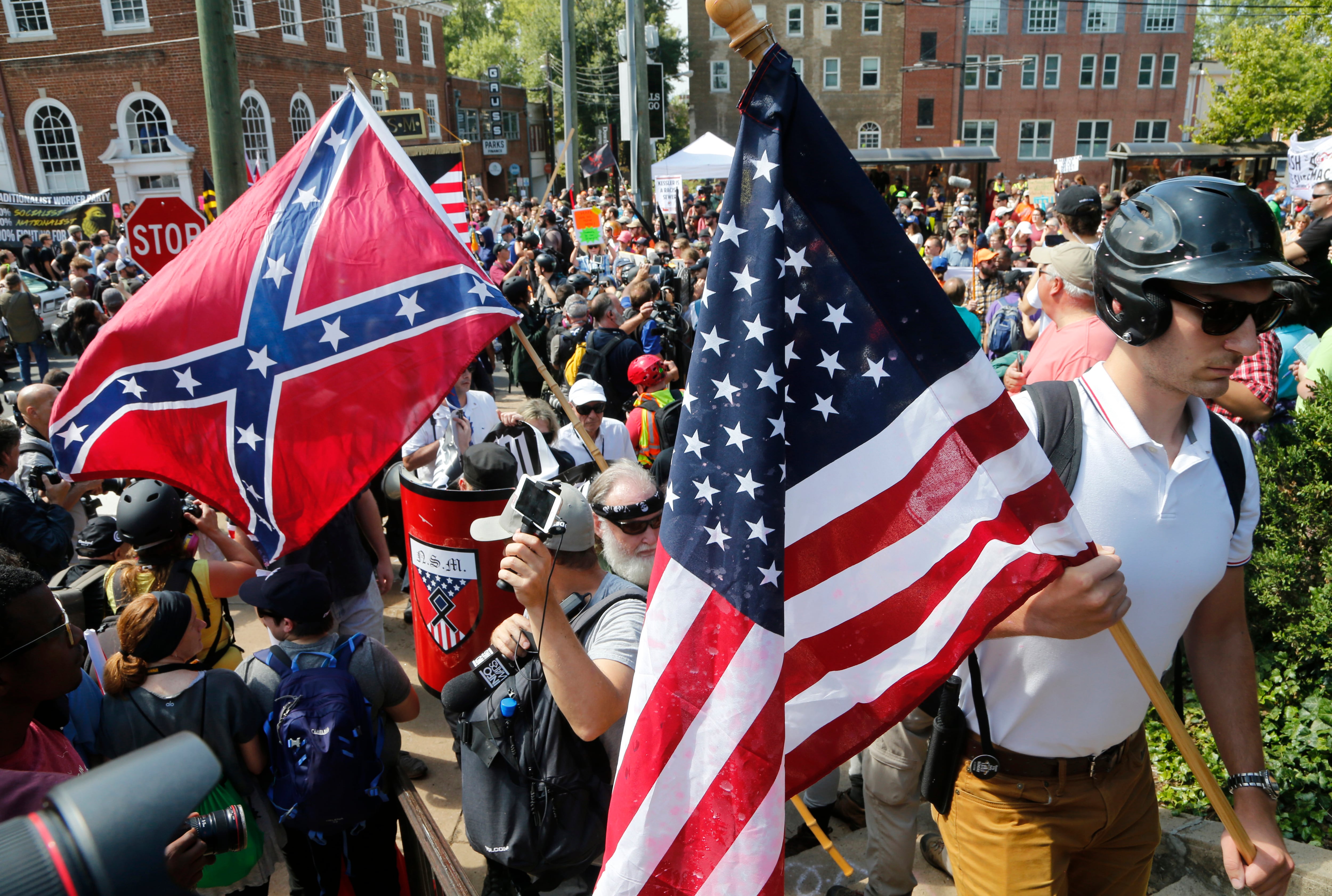

Research institutions such as the Institute for Strategic Dialogue found that Discord serves as a hub for socializing and community-building across far-right groups, including Catholic extremists, the white supremacist Atomwaffen Division and the antigovernment Boogaloo movement.
Extremist groups value the platform’s layers of privacy and anonymity, as well as its chat and video functions and collaborative nature, Guhl said. Berge described it as a walled garden, or an online environment where user access to content can be controlled. Servers come with the capability to assign hierarchy to different members and allow some members to access information that others can’t, the researchers said.
“In, say, a Twitter direct-messaging thread or Facebook DM, you don’t really have levels and hierarchies,” Squire said. “Discord really allows you to have more fine-grained ranking structures.”
Another reason for the prevalence of extremists on the platform stems from its roots in gaming, Guhl surmised.
Rachel Kowert, a globally recognized researcher on gaming and mental health, has spent five years researching extremism in video game communities. Though gaming itself is a powerful tool for connection and growth, extreme and hateful ideologies are now commonplace in those spaces, Kowert said.
“If you’re spending a lot of time in the social or gaming spaces where misogyny is commonplace, that can in turn start to internalize in the way you see the world and interact in it,” Kowert said.
Fighting a dark legacy
The existence of far-right groups on Discord — and the high-profile instances of extremism on the platform in the past several years — has spawned its “extremist legacy,” one from which it’s now trying hard to distance itself, said Berge.
Discord said it removed more than 2,000 far-right-affiliated servers following the “Unite the Right” rally. After the Buffalo killings, it removed Gendron’s server and worked to prevent the spread of content related to the attack, the company said. At that point, Discord agreed it “must do more to remove hate and violent extremism.”

“We created Discord to be a place for people to find belonging, and hate and violence are in direct opposition to our mission,” the company said in a statement at the time. “We take our commitment to these principles seriously and will continue to invest in and deploy resources.”
Earlier this year, the company reported that 15% of its staff works on its user safety team, which cracks down on harassment, hateful conduct, inappropriate contact, violent and abusive imagery, violent extremism, misinformation, spam, fraud, scams and other illegal behavior.
During the investigations into Teixeira and Jason Gray, Discord officials immediately cooperated with law enforcement, a company spokesperson told Military Times. And in recent months, Discord has leaned on machine-learning technology to moderate content.
“We expressly prohibit using Discord for illegal activity, which includes the unauthorized disclosure of classified documents,” the spokesperson said.
The company publishes reports each quarter showing actions taken against various accounts and servers. The latest report, published in January, says Discord disabled 6,109 accounts and removed 627 servers that espoused violent extremism during the last few months of 2023.
Squire and Guhl agreed that Discord is “pretty good” at responding to extremist content. Guhl credited the company for including extremism and hate speech in its community guidelines, as well as for deleting servers on a regular basis that breach its terms of service. Discord also created a channel where Squire could flag questionable content on the platform, and the company has been receptive to the concerns she’s raised, she said.
“I credit where credit is due, and I have to give them credit for that,” Squire said. “I think it’s taken seriously, and there are other platforms that I could not say that about.”
Extremists are ‘absolutely still there’
Berge applauded Discord for ramping up the technology behind its moderation and for introducing IP bans, which restrict a device from accessing the platform, rather than just an account. Still, she sees room for improvement.
Discord should place more emphasis on educating moderators and users about how to recognize when someone is being radicalized and pulled into an extremist space, Berge said. She also criticized the platform for disbanding a program in 2023 that included hundreds of volunteer moderators.
“It wasn’t Discord’s automated flagging systems that caught national security secrets being leaked by Jack Teixeira. It took other users and community moderators digging into it and someone finally reporting it,” Berge said. “Elevating people and giving them tools to moderate is absolutely central to protecting the platform, and that’s one area where I think they’re taking a step back.”
Berge is still researching communities on Discord, four years after she first uncovered a network of white supremacists using the platform as a recruitment ground. Despite its community guidelines and efforts to remove offending servers and accounts, Discord still serves as a meeting place for pockets of extremism.
“They’re harder to find, but they are absolutely still here. We’re still finding them,” Berge said. “It is still one of the most popular spaces for people to congregate, share and be in community with each other, for better or for worse.”
Discord remains the “platform of choice” for some hate groups, noted Squire, who described the company’s fight against extremists as playing whack-a-mole: As soon as one is removed, another pops up. A lack of institutional knowledge among far-right extremist groups is partly to blame, she said.
“Everybody’s always fresh, and they don’t have any structure for teaching one another and learning from mistakes of the past,” Squire said. “That’s convenient for us, because as we keep amassing knowledge, they make the mistake of reusing the technology that’s most convenient, rather than being strategic.”
This story was produced in partnership with Military Veterans in Journalism. Please send tips to MVJ-Tips@militarytimes.com.
Nikki Wentling is a senior editor at Military Times. She's reported on veterans and military communities for nearly a decade and has also covered technology, politics, health care and crime. Her work has earned multiple honors from the National Coalition for Homeless Veterans, the Arkansas Associated Press Managing Editors and others.





